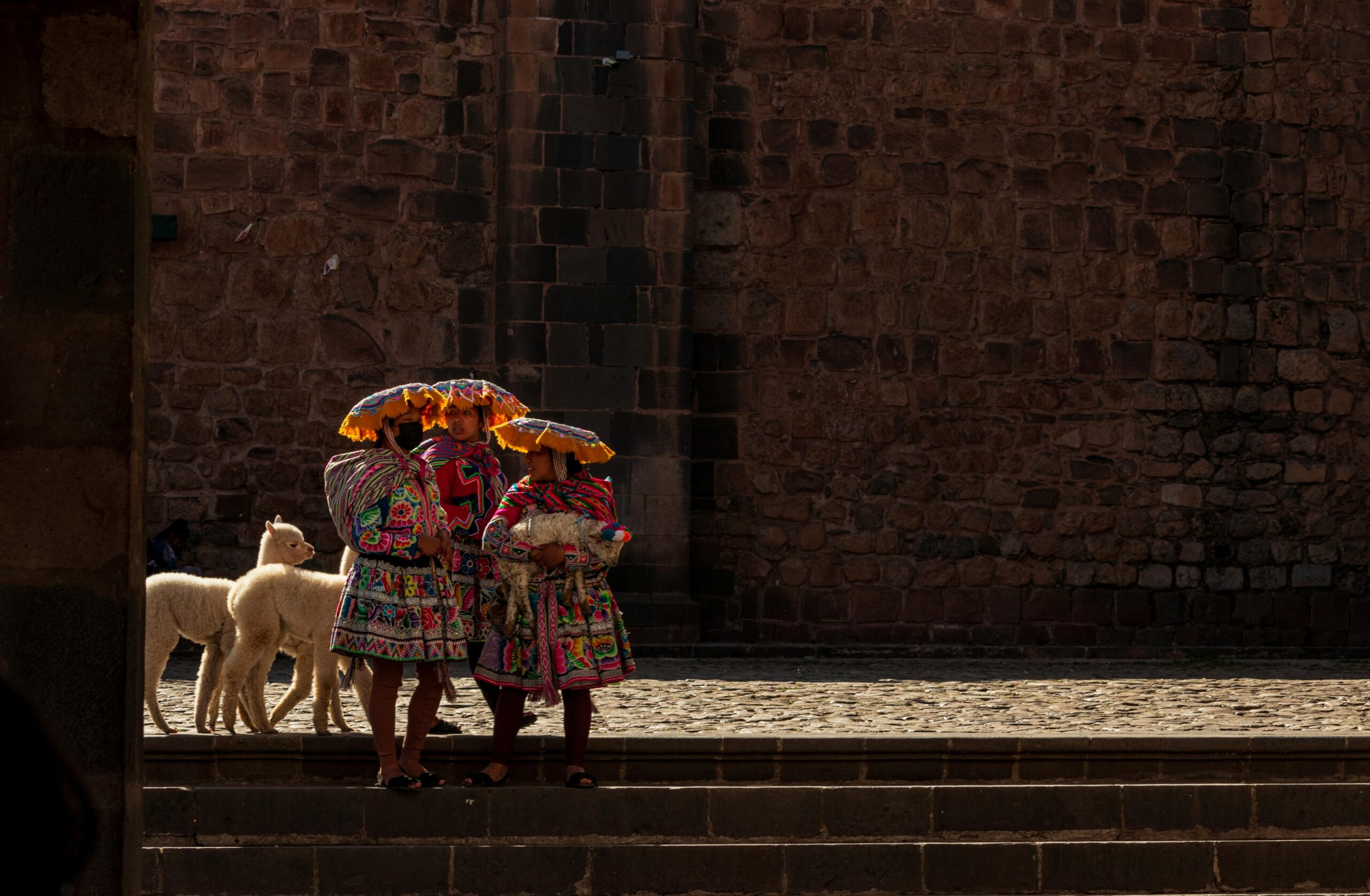Coevolution of sheep and humans over millennia(10,000 years old period).
By studying ancient DNA, we have found that sheep and humans have been co-evolved. Biology of sheep has an important role in shaping the human civilization. It has helped explain, the human history, culture and survival. Different international research teams from different academic backgrounds including geneticists and archaeologists and zoologist, have found that both sheep and human are closely living together for over 11,000 years.
They analyzed such results by studying 118 genomes by collecting samples from archeological old bones which were 12 thousand years old found from Mongolia to Ireland. They could come up results with findings about the village named Aşıklı Höyük located in central Turkey. It was place where the sheep were fist domesticated and confirmed their ancestry from the wild mouflon.
We can say that ancient DNA has played much important role in understanding the linked history of sheep and human livelihoods. Over the past 11,000 years, sheep have been one of humanity’s most important domesticated animals, providing wool, meat, milk, and other resources.
Ancient DNA studies have shed light on how sheep have evolved alongside humans, answering the deep genetic changes that occurred during domestication and the spread of sheep across the world.
Ancient DNA from sheep bones and teeth found at archaeological sites has provided details about human migration and trade routes. i.e., genetic studies have shown how sheep populations spread with Early European farmers into Asia, explained the movement of human populations and their agricultural practices. This genetic evidence proves the role of sheep in the extension of early human civilizations.
Ancient DNA found how sheep genetically adapted to different environments and human management practices over millennia. i.e., genetic markers linked with wool production, disease resistance, and climate adaptation showed how humans shaped sheep to meet their needs. These adaptations were not just physical but also genetic, as humans selectively bred sheep for specific traits.
The genetic history of sheep also explained their cultural and economic importance to ancient societies. Ancient DNA studies have uncovered evidence of specialized breeding for wool in certain regions, such as the fine wool sheep of ancient Mesopotamia, which were valuable for textile production. This draw attention towards the deep connection between sheep and human economic systems.
Ancient DNA tells us that how sheep populations survived and adapted to challenges such as climate change, disease, and human conflict. And now can easily understand how these species have helped human in those tough situations.
This study is published in Journal Science.